Satellite Based Augmentation Systems
For applications where the cost of a differential GNSS system is not justified, or if the rover stations are spread over too large an area, a Satellite Based Augmentation System (SBAS) may be more appropriate for enhancing position accuracy.
SBAS systems are geosynchronous satellite systems that provide services for improving the accuracy, integrity and availability of basic GNSS signals.
- Accuracy is enhanced through the transmission of wide-area corrections for GNSS range errors.
- Integrity is enhanced by the SBAS network quickly detecting satellite signal errors and sending alerts to receivers that they should not track the failed satellite.
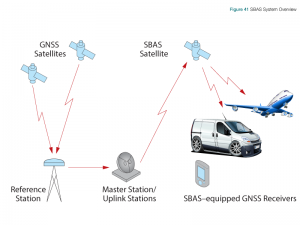
- Signal availability can be improved if the SBAS transmits ranging signals from its satellites. SBAS systems include reference stations, master stations, uplink stations and geosynchronous satellites, as shown in Figure 41.
Reference stations, which are geographically distributed throughout the SBAS service area, receive GNSS signals and forward them to the master station. Since the locations of the reference stations are accurately known, the master station can accurately calculate wide-area corrections.
Corrections are uplinked to the SBAS satellite then broadcast to GNSS receivers throughout the SBAS coverage area.
User equipment receives the corrections and applies them to range calculations.
The following sections provide an overview of some of the SBAS services that have been implemented around the world or that are planned.
Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS)
The US Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has developed the Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) to provide GPS corrections and a certified level of integrity to the aviation industry, to enable aircraft to conduct precision approaches to airports. The corrections are also available free of charge to civilian users in North America.
A Wide Area Master Station (WMS) receives GPS data from Wide Area Reference Stations (WRS) located throughout the United States. The WMS calculates differential corrections then uplinks these to two WAAS geostationary satellites for broadcast across the United States.
Separate corrections are calculated for ionospheric delay, satellite timing, and satellite orbits, which allows error corrections to be processed separately, if appropriate, by the user application.
WAAS broadcasts correction data on the same frequency as GPS, which allows for the use of the same receiver and antenna equipment as that used for GPS. To receive correction data, user equipment must have line of sight to one of the WAAS satellites.
European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS)
The European Space Agency, in cooperation with the European Commission (EC) and EUROCONTROL (European Organization for the Safety of Air Navigation) has developed the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS), an augmentation system that improves the accuracy of positions derived from GPS signals and alerts users about the reliability of the GPS signals.
Three EGNOS satellites cover European Union member nations and several other countries in Europe. EGNOS transmits differential correction data for public use and has been certified for safety-of-life applications. EGNOS satellites have also been placed over the eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and the African mid-continent.
MTSAT Satellite Based Augmentation Navigation System (MSAS)
MSAS is an SBAS that provides augmentation services to Japan. It uses two Multi-functional Transport Satellites (MTSAT) and a network of ground stations to augment GPS signals in Japan.
GPS-Aided GEO Augmented Navigation System (GAGAN)
GAGAN is an SBAS that supports flight navigation over Indian airspace. The system is based on three geostationary satellites, 15 reference stations installed throughout India, three uplink stations and two control centers. GAGAN is compatible with other SBAS systems, such as WAAS, EGNOS and MSAS.
System for Differential Corrections and Monitoring (SDCM)
The Russian Federation is developing SDCM to provide Russia with accuracy improvements and integrity monitoring for both the GLONASS and GPS navigation systems. By 2016, the Russian Federation plans to provide L1 SBAS coverage for all Russian territory and by 2018 L1/L5 coverage. SDCM will also provide Precise Point Positioning (PPP) services for L1/L3 GLONASS by 2018.
Other SBAS Systems
China is planning SNAS (Satellite Navigation Augmentation System), to provide WAAS-like service for the China region.
Ground Based Augmentation System
A Ground Based Augmentation System (GBAS) provides differential corrections and satellite integrity monitoring to receivers using a VHF radio link. Also known as a Local Area Augmentation System (LAAS), a GBAS consists of several GNSS antennas placed at known locations, a central control system and a VHF radio transmitter.
GBAS covers a relatively small area (by GNSS standards) and is used for applications that require high levels of accuracy, availability and integrity. Airports are an example of a GBAS application.